Cervical cancer develops in the cervix. This cancer is usually caused by a virus called HPV, which can be caused by sexual contact. Generally, there are no visible symptoms due to which it is not detected on time. If it is not treated on time then it becomes fatal. Therefore, every woman should pay attention to the changes occurring in the body. So that cervical cancer can be detected at the right time. Let us tell you that World Cancer Day (World Cancer Day 2024) is celebrated all over the world on 4 February. Let us know in detail about cervical cancer.
Table of Contents
Cervical cancer is a serious health problem not only in India but for women all over the world. This cancer occurs in the cervix cells which are the lower part of the uterus, which connects to the vagina. Some people also know it as cervical cancer. This cancer is caused by a special type of HPV, a sexually transmitted infection.
What is HPV?
Human papilloma virus (HPV) is a group of viruses, of which there are more than 100 types and about 30 types can affect the genital area. Of these, 14 are cancer causing, which have been classified as high risk HPV. Two types of this virus cause 70 percent of cervical cancer and cervical lesions. According to reports, about 80% of sexually active people come in contact with HPV infection at least once in their lifetime. For some people it gets better soon. So in some women it becomes the cause of cancer.
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
Generally, no symptoms are visible until cervical cancer reaches the advanced stage. But in the advanced stage, it also starts spreading to other parts of the body including the liver, bladder, vagina, and rectum. In which symptoms are visible.
Its symptoms may include
1. Irregular menstruation
2.Vaginal bleeding
3.Absence of vagina
4.pain in the lower abdomen
5.Unbearable pain in pelvic or lower back
6.Weight loss without any reason.
This cancer can be detected and treated if detected early.
Reasons of cervical cancer?
1.HPV Infection: The most important reason is infection with a virus called HPV, which is the main reason behind most cervical cancers. This virus spreads through sexual contact.
2.Smoking: The risk of cervical cancer increases in women who smoke.
3.Weak immune system: Women with weak immune system have an increased risk of getting HPV infection, which also increases the risk of cervical cancer.
4.History of cancer in the family: If a woman has a history of cervical cancer in her family, her risk increases further.
5.Adult sex: The risk of cervical cancer increases as you start having sex as you reach adulthood.
Along with these reasons, there can be many other factors which play a role in the development of cervical cancer.
Stages of Cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is often classified into stages based on the extent of the disease. The staging system helps determine the appropriate treatment approach. Here’s an overview of the stages and their impact on treatment options
1.Stage 0 (Carcinoma in situ)
This is the earliest stage, where abnormal cells are found only on the surface of the cervix.
Treatment often involves removing the abnormal cells through procedures like cone biopsy or loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP).
2.Stage I (Early-stage cancer)
Cancer is confined to the cervix.
Treatment options may include surgery (such as hysterectomy or trachelectomy) or radiation therapy.
3.Stage II (Locally advanced cancer)
Cancer has spread beyond the cervix to nearby tissues but is still within the pelvic area.
Treatment may involve a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and sometimes chemotherapy.
4.Stage III (Advanced cancer)
Cancer has spread to the lower third of the vagina or the pelvic wall and may cause kidney problems.
Treatment often includes a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
5.Stage IV (Metastatic cancer)
Cancer has spread to distant organs, such as the bladder, rectum, or beyond the pelvic area.
Treatment may involve a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies.
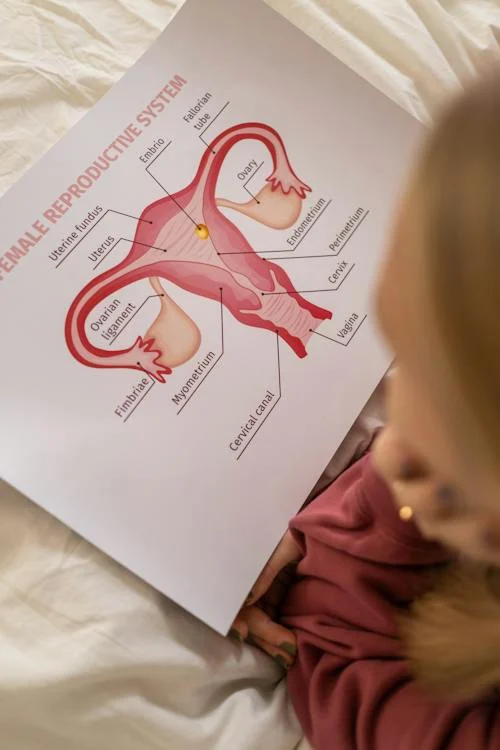
Prevention of Cervical cancer
1.Regular screening and vaccine are necessary: To prevent cervical cancer, all girls and women above 20 years of age should do regular screening. With this, it becomes known at the right time. Vaccines also exist to prevent this cancer. Therefore, it should also be used by women and girls.
2.Surgery: In the early stages of cervical cancer, doctors often suggest surgery to remove the tumor. For this, according to the program, either the tumor near the uterus is removed in the primary stages of cervical cancer or the entire uterus is removed.
3.Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy can also be an option for the treatment of cervical cancer. This may be appropriate for patients who are not considered candidates for surgery or who have some other reason for having surgery.
4.Chemotherapy: In many cases, chemotherapy is used as a treatment for cervical cancer, especially if the cancer has spread. This is done to destroy cancer by using medicines.
5.Medications: There are several specific medications used that can help treat cervical cancer, such as targeted therapy and immunotherapy. These treatments should be started only under the consultation and discipline of the doctor. They should be guided towards medical testing and correct treatment.
6.Safe sexual relationship: Cervical cancer is caused by HPV and other STDs. Therefore, keep safety in mind while having a sexual relationship with your partner. Use measures like condoms.
7.Healthy Diet: Do not smoke and consume alcohol at all. Take a diet that strengthens immunity. Include fruits, vegetables and whole grains in your diet. Reduce weight and do regular exercise.
The choice of treatment is influenced by various factors, including the stage of cancer, the patient’s overall health, and personal preferences. In some cases, a multidisciplinary approach combining surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy may be recommended. It’s essential for individuals diagnosed with cervical cancer to consult with their healthcare team to determine the most suitable treatment plan based on their specific situation. Early detection and personalized treatment play crucial roles in improving outcomes for individuals with cervical cancer.

